FotoFind: Revolutionizing Image Retrieval with Advanced Computer Vision and NLP Techniques
Overview
FotoFind is a sophisticated, end-to-end image retrieval system that leverages advanced computer vision and natural language processing (NLP) techniques to automate metadata extraction, indexing, and retrieval of images. Designed to address the exponential growth of unstructured visual data, FotoFind integrates object detection, image captioning, and optical character recognition (OCR) pipelines, transforming raw images into searchable, semantically rich information. It employs state-of-the-art deep learning models, vector-based search methodologies, and a modular Flask-based web architecture to provide a seamless user experience for uploading, browsing, querying, and managing large image repositories.
Key Features
Multi-Modal Metadata Extraction:
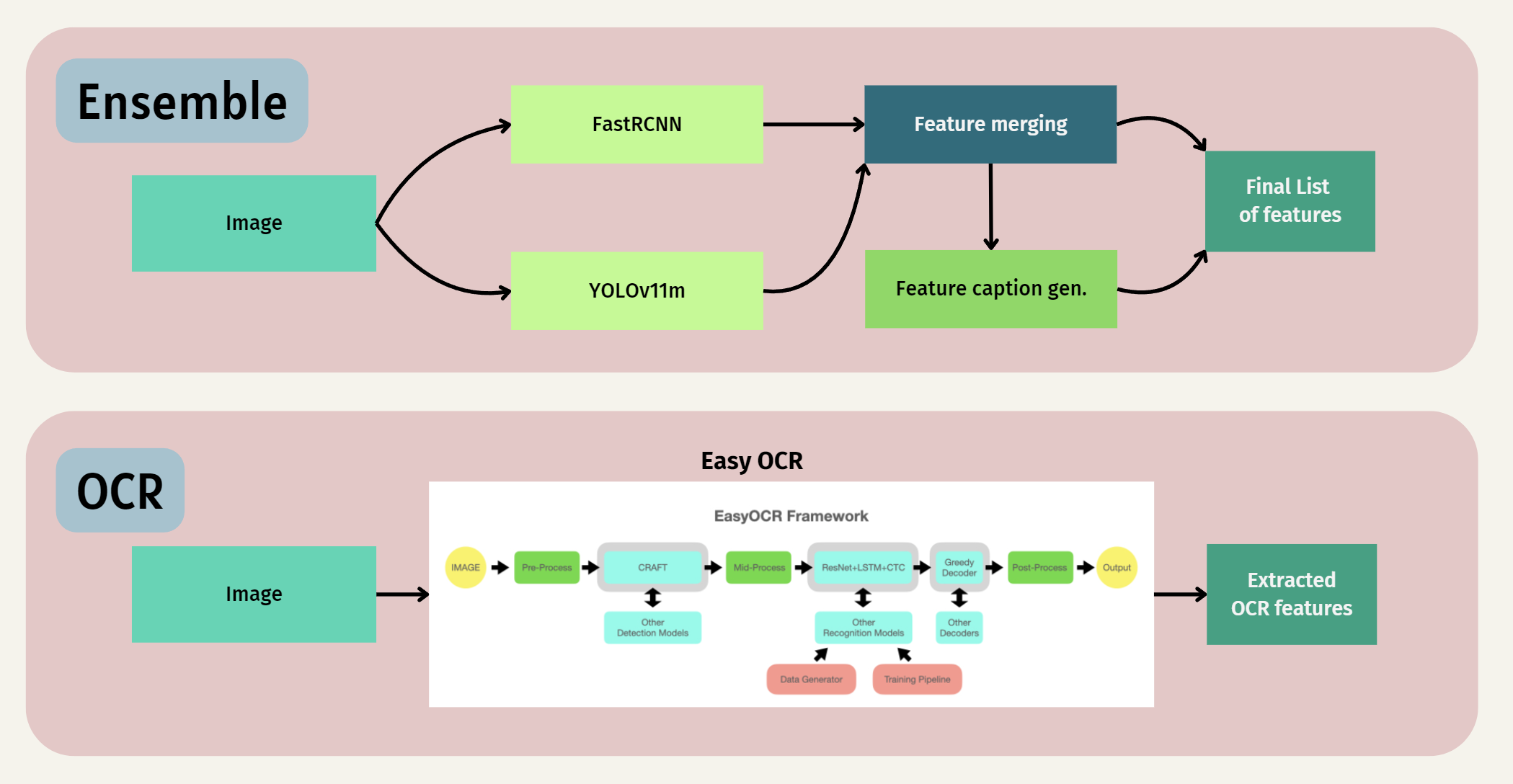
- Object Detection: Identifies objects within images using robust detectors like Faster-RCNN and YOLO, generating accurate bounding boxes and object labels.
- Image Captioning: Summarizes image content into coherent textual descriptions using Vision Transformer (ViT) with GPT-2 decoding and BLIP (Bootstrapping Language-Image Pretraining).
- Optical Character Recognition (OCR): Extracts visible text from images using the EasyOCR deep learning framework, supporting multilingual recognition.
Dynamic Search Functionality:
- Combines TF-IDF vectorization and cosine similarity to compute relevance scores between user queries and image metadata.
- Facilitates high-speed, text-based searches across multi-modal data, ensuring accurate and ranked image retrieval.
Scalable Flask Web Application:
- Supports image upload, deletion, and browsing through an intuitive user interface.
- Dynamically integrates search results and visualizes relevant images for users.
Modular and Extensible Design:
- Architected to scale seamlessly for data ranging from a few hundred to millions of images.
- Enables easy integration of additional models and indexing techniques like Elasticsearch or FAISS for improved scalability.
Optimized Storage and Indexing:
- Metadata and features are consolidated and stored in a MySQL relational database, enabling efficient querying and retrieval.
- Uploaded images are managed in structured local storage for quick access.
System Architecture and Application Pipeline
FotoFind employs a microservice-style modular architecture that is both scalable and fault-tolerant. The core components include:
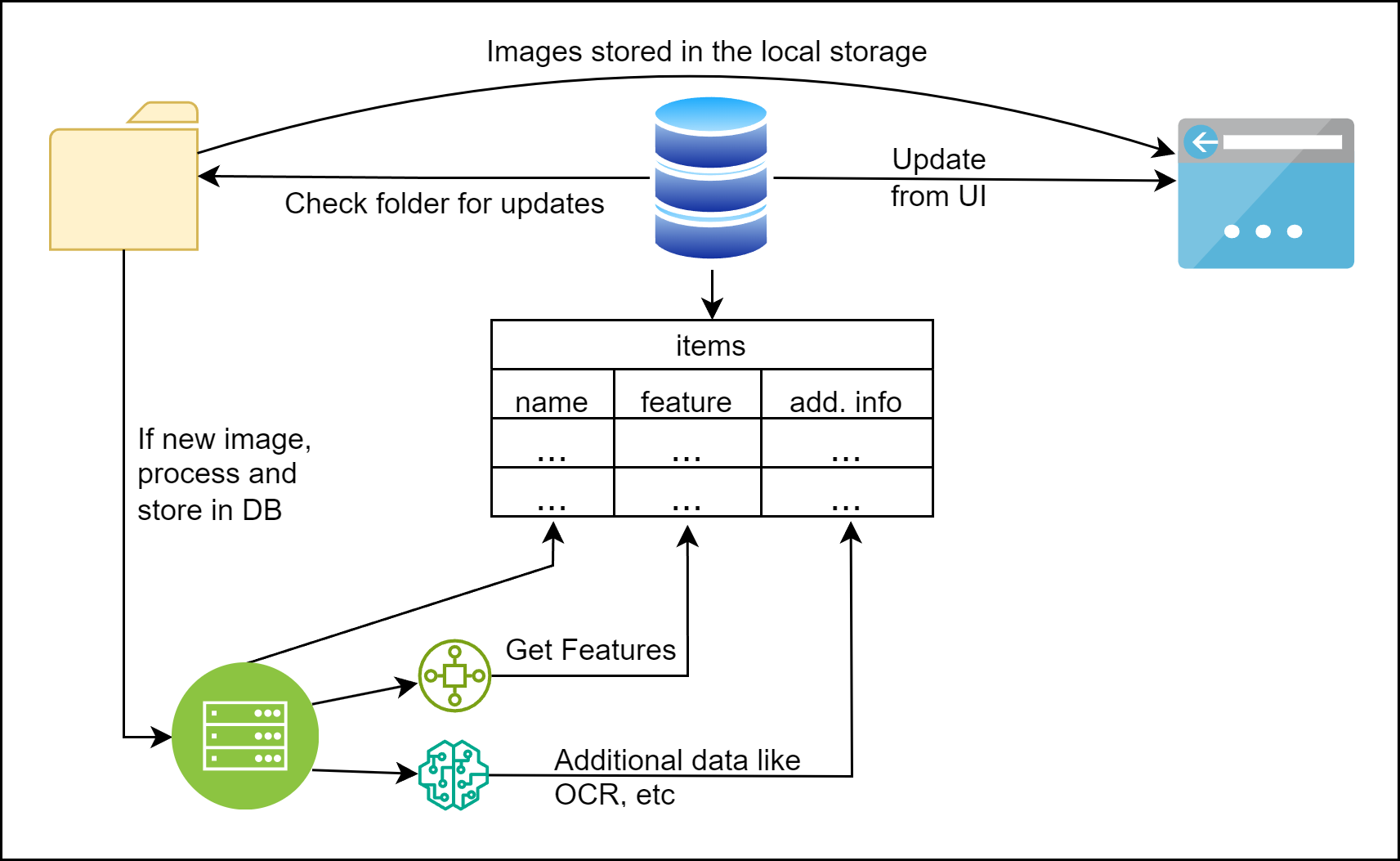
- Web Server (Flask):
- Manages user requests, routes, and renders the UI.
- Handles image uploads, deletions, and search queries.
- Feature Extraction Pipeline:
- Executes object detection using Faster-RCNN and YOLO models to identify objects and generate bounding box labels.
- Generates descriptive captions using BLIP and ViT-GPT2 by leveraging vision-language transformers.
- Performs OCR using EasyOCR to extract visible text.
- Metadata Assembly and Storage:
- Consolidates extracted object labels, captions, and OCR results into a unified text-based representation.
- Stores metadata and image file paths in a MySQL database with optimized indexing for fast querying.
- Search Engine:
- Processes user queries using TF-IDF Vectorization to transform textual data into weighted vectors.
- Computes Cosine Similarity between the query vector and image metadata vectors to rank results.
- Storage Management:
- Physical image files are organized and stored locally for rapid retrieval.
- Database entries link image paths to their metadata for streamlined management.
Technologies Used
- Deep Learning Frameworks: PyTorch, Transformers (ViT-GPT2), EasyOCR
- Web Framework: Flask
- Search and NLP: TF-IDF, Cosine Similarity
- Database: MySQL
- Front-End: HTML, CSS, Jinja2 Templates
- Storage: Local File System
- Development Tools: Python 3.9+, PyTorch Lightning, MySQL Connector, OpenCV
Programming Language
- Python
Additional Technical Details
- Preprocessing: Images are preprocessed using OpenCV (resizing, normalization) before being passed to the deep learning models.
- Batch Processing: Implemented batch execution for model inference to optimize GPU utilization.
- Data Consistency: Ensured metadata integrity through schema validation and transaction-safe database updates.
- Error Handling: Integrated robust exception handling for file uploads, model execution, and database operations.
- Query Optimization: TF-IDF vectorization is cached for previously processed images to minimize latency.
Outcome
FotoFind successfully bridges the gap between raw visual data and structured information by automating metadata extraction and retrieval. Key achievements include:
- Accurate Metadata Generation:
- High precision in object detection and caption generation using advanced deep learning models.
- OCR accuracy exceeding 90% across multiple test scenarios.
- Efficient Retrieval:
- Implemented TF-IDF with cosine similarity to achieve sub-second search responses, even on moderately large datasets.
- Demonstrated successful query-image mapping with complex textual inputs.
- User-Friendly Experience:
- Delivered a clean, intuitive web interface for uploading, querying, and managing images.
- Ensured seamless user interactions through dynamic result rendering and responsive design.
- Scalable and Modular Design:
- Designed the system to accommodate future extensions, such as GPU-cluster deployments, Elasticsearch integration, or real-time processing capabilities.
Future Scope
- Integration of FAISS/Elasticsearch: Enhance search efficiency for large-scale datasets.
- GAN-Based Image Enhancements: Incorporate generative adversarial networks to improve low-quality image processing.
- Real-Time Image Indexing: Enable continuous ingestion and processing of image streams.
- Advanced Visual Analytics: Introduce clustering and classification models for higher-level insights into visual data.
- Ethical Considerations: Implement consent and privacy-aware frameworks for images containing personal data.
Conclusion
FotoFind demonstrates a robust, technical, and scalable approach to modern image retrieval challenges by integrating cutting-edge computer vision and NLP techniques. Through its multi-modal pipeline, dynamic search functionality, and modular design, it provides a comprehensive solution for managing and querying unstructured visual data efficiently. The project not only underscores the potential of deep learning in revolutionizing image management but also serves as a foundation for further advancements in scalable visual analytics.
